Deploy containerized applications
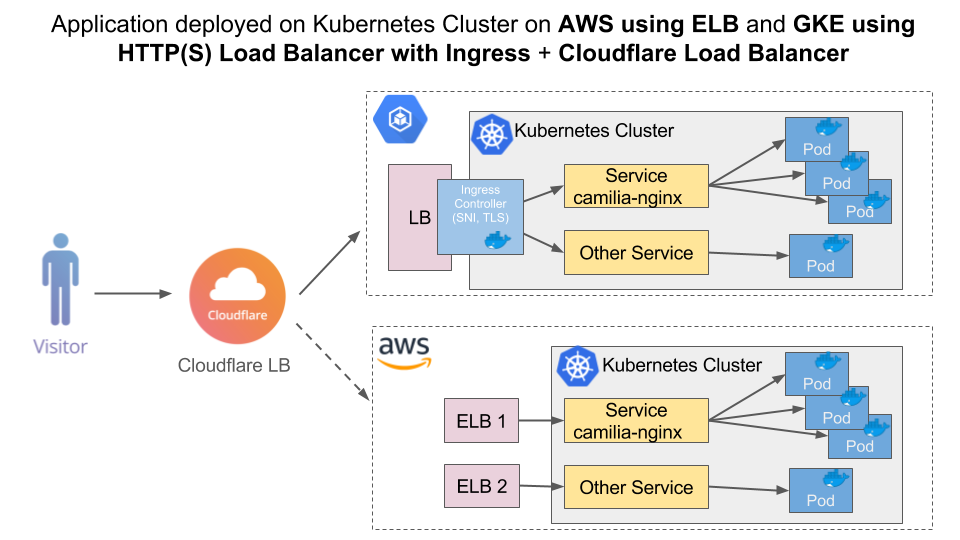
Cloudflare’s Load Balancer distributes global traffic intelligently across Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) and Amazon Web Services EC2 (AWS). Cloudflare’s native Kubernetes support provides a multi-cloud deployment that is transparent to end users.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, be sure you have the following:
- Access to Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Access to AWS
- Docker image
- A domain on Cloudflare (on the Free, Pro, or Business plan) with a Load Balancing subscription, configurable in Traffic on the dashboard
Deploying a containerized web application on Google Kubernetes Engine
You will be using Google Cloud Shell interface, which comes preinstalled with the gcloud console, docker, and kubectl command-line tools used below. If you use Cloud Shell, you do not need to install these command-line tools on your workstation.
Getting started
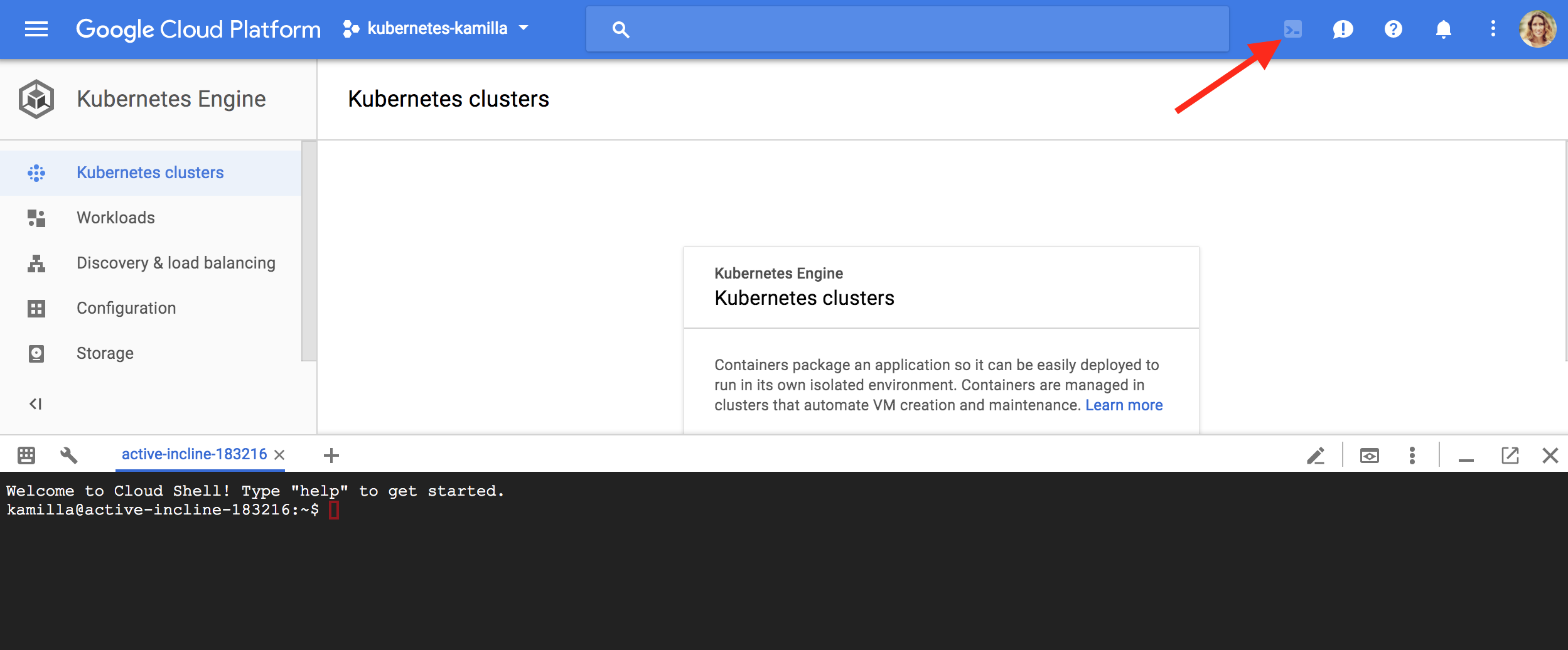
Go to the Kubernetes Engine. Click the Activate Google Cloud Shell button at the top of the console window. A Cloud Shell session with a command prompt will open in a new frame at the bottom of the console.
Set default configuration values by running the following commands:
gcloud config set project PROJECT_IDgcloud config set compute/zone us-west1-a
Deploying a web application
Create a container cluster to run the container image. A cluster consists of a pool of Compute Engine VM instances running Kubernetes.
Run the following command to create a three-node cluster (our cluster name is camilia-cluster):
gcloud container clusters create camilia-cluster --num-nodes=3It may take several minutes for the cluster to be created. Once the command is complete, run the following command to see the cluster’s three worker VM instances:
gcloud compute instances list
Deploy the application to the cluster. Use the kubectl command-line tool to deploy and manage applications on a Kubernetes Engine cluster. You can create a simple nginx docker container, for example, using the following command (camilia-nginx is the name for the deployment):
kubectl run camilia-nginx --image=nginx --port 80